Nmap
Start with a fast scan to check for open ports and than run a full scan only on them.
Fast scan, requires priviliges:
nmap -sS <HOST>
nmap -sS 10.10.1.1
Advanced scannning on specific ports:
nmap -p <PORTS> -A <HOST>
nmap -p 22,80,443 -A 10.10.1.1
Usually, it is better to run nmap with verbose output to see what is happening by adding the -v or -vv flag to the command.
By default, nmap scans the first 1000 ports.
To scan all the 65535 ports use the -p- flag.:
nmap -sS -p- <HOST>
nmap -sS -p- 10.10.1.1
TCP scan
TCP scan is the default scan type when nmap is run without priviliges.
nmap -sT <HOST>
nmap -sT 10.10.1.1
It is slower than the SYN scan but it is more reliable.
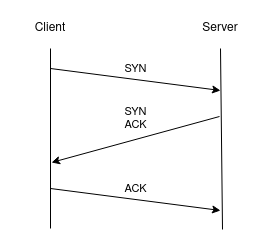
Each port is checked through a complete three-way handshake.
SYN scan
SYN scan is the default scan type when nmap is run with priviliges.
nmap -sS <HOST>
nmap -sS 10.10.1.1
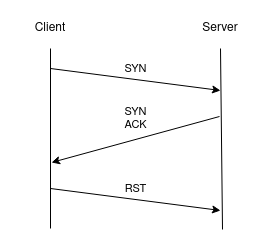
It is faster than TCP scan because it does not complete the three-way handshake.
Each port is checked by sending a SYN packet and waiting for a SYN/ACK response.
Half way handshake is based on the fact that the host will respond with a SYN/ACK packet only if the port is open.
nmap will respond with a RST packet to close the connection.
Other types of scan
-sF- FIN scan - Send a FIN packet to close the connection.-sX- XMAS scan - Send a FIN, URG and PUSH packet to close the connection.-sN- NULL scan - Send an empty packet to close the connection.-sA- ACK scan - Send an ACK packet to check if the port is filtered or not.-sU- UDP scan - Send a UDP packet to check if the port is open or not.
Ports result
There are three possible results for a port:
open- The port is open and accepting connections.closed- The port is closed and not accepting connections.filtered- The port is not responding to Nmap's probes, maybe a firewall is blocking it.
Stealth
nmap -sA --disable-arp-ping -T 1 -n <HOST>
Using a specific DNS service on the host
nmap -source-port DNS_PORT <HOST>