Introduction to ML
Machine Learning focuses on the development of computer programs that can change when exposed to new data.
Machine Learning can be divided into three main paradigms:
- Supervised Learning
- Unsupervised Learning
- Reinforcement Learning
Supervised Learning
In supervised learning the computer is presented with example inputs and their desired outputs and the goal is to learn a general rule that maps inputs to outputs.
The training is based on already labeled data and the goal it to categorize new data.
There are two types of supervised learning problems:
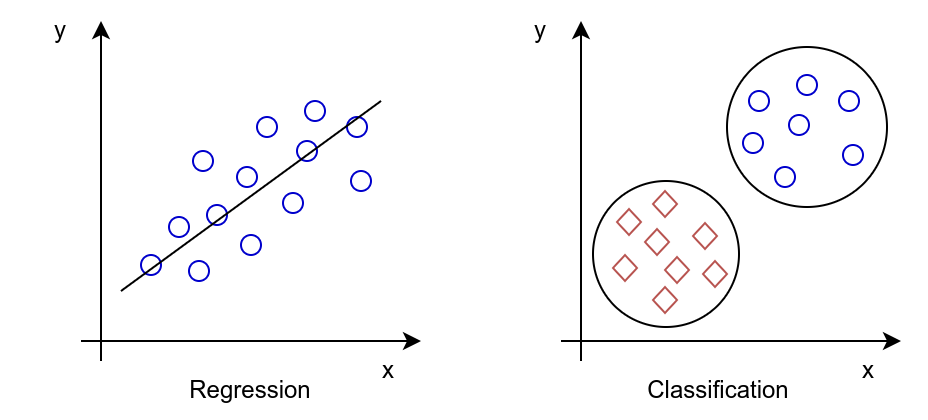
- Classification: the goal is to predict the category of the input data.
- Regression: the goal is to predict a number based on the input data.
In classification there is a small number of possible outputs, while in regression the possible output can be infinite.
Unsupervised Learning
In unsupervised learning the computer is presented with a set of inputs and the goal is to find patterns in the data.
The training is based on unlabeled data and the goal is to categorize the data based on similarities and differences.
There are three types of unsupervised learning problems:
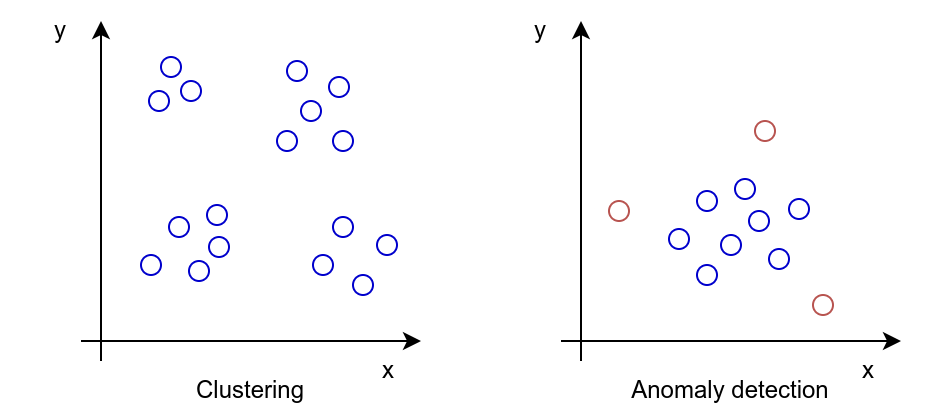
- Clustering: the goal is to group similar data points together.
- Anomaly detection: the goal is to identify data points that are different from the rest.
- Dimensionality reduction: the goal is to reduce the number of input variables.
Reinforcement Learning
In reinforcement learning the computer is programmed to take specific actions in a specific environment and the goal is to maximize some notion of cumulative reward.
The training is based on the interaction with the environment and the goal is to learn the best action to take in a given situation.
The computer is not told which action to take, but instead it must discover which action will yield the most reward by trying them.